News Update
Yesterday evening Jasmine Wietzke (Department of Fisheries and Ocean - Institute of Ocean Sciences, DFO-IOS) entertained some of the ships crew and science staff playing guitar and singing several cover and original tunes. 

For you birders out there, a small flock of 6-8 Ross' Gulls were spotted this morning. According to Chief Scientist – very rare. They were spotted right at the ice margin where we crossed into the more open water. This is where there is typically an abundance of zooplankton that the gulls feed on. I tried to take some pictures but had removed the memory card earlier: no memory card, no pictures.
Chemistry Timeout
So last time we talked about the dissociation of carbonic acid: H2CO3 ––> 2H+ + CO32-. In this change 2 H+ ions are formed. The next reaction that takes place is probably one of the most important chemical reactions EVER. It involves the H+ ions from the previous reaction and water molecules, abundant because all of this is taking place in a solution mostly made up of water. The reaction goes like this: H+ + H2O ––> H3O+. The H3O+ can be a rare bird (not to be confused with Ross' Gull) and it is called the hydronium ion. The amount of hydronium ions present in a solution will then dictate how acidic or basic a solution is. And you guessed it... we'll hit that next time.
Crew Member Focus
Sheridan Rice is an Oiler on the Louis St. Laurent and was born, raised and still lives in Twillingate, Newfoundland home. Twillingate is a small village (population 2000) on a small island north of St. Johns. His village was a fishing community up until the cod moratorium put in place in the mid 1980's. Sheridan is in his first year in the Coast Guard with this cruise being his second shift. He anticipates being in for the long haul because the job offers long-term consistent employment doing work that he enjoys. Sheridan has a set of meaty hands which clearly love to "fix stuff". He says he loves figuring out what is wrong with something and then tearing it down and repairing it. As an Oiler, Sheridan and the rest of the engine room crew do lots of routine inspections and maintenance of all things power plant related.


Geo-engineering Methods to Improve Arctic ClimateThe average weather over a particular region of the Earth. Climate originates in recurring weather phenomenon that result from specific types of atmospheric circulation. (cooling down)
If you agree that building a dam in Bering Strait and that deploying powerful icebreakers to the Arctic Ocean to move ice out are realistic ideas, then our method shown in the following schematic is also realistic. We propose to build a floating dam in Fram Strait and/or deploy icebreakers to keep sea ice in the Arctic Ocean.
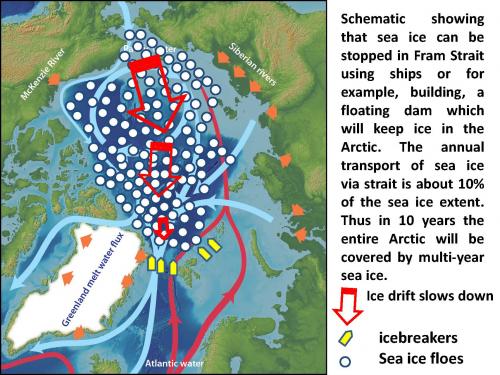
Observations show that sea ice is transported from the Arctic Ocean to the North Atlantic via Fram Strait. The annual areal loss of ice through this strait is around 800,000 km per year. This represents 10% of the annual sea ice extent (around 8 million km2) in the Arctic region bounded by 65˚N latitude. This graph shows that sea ice extent in the Arctic Ocean is decreasing rapidly and that at the same time there is the increasing areal transport of sea ice from the Arctic Ocean to the Greenland Sea. 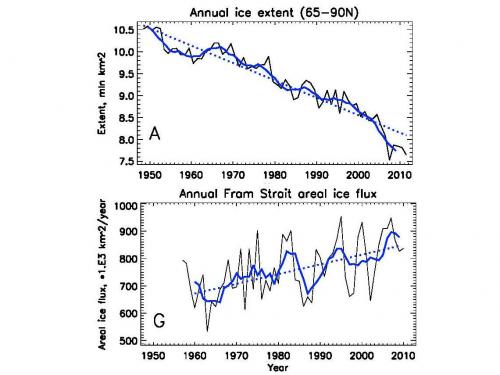
The daily cost of a single icebreaker’s work is around $100,000; annual is around $37 million so $370 million for 10 years. The width of the Fram Strait is 500 km and if 500 icebreakers (one per 1 km) would be deployed than the cost of the whole project would be only $185 billion dollars which is significantly less than $500 billion dollars per year needed for realization of the “wind-powered pumping” project. Theoretically, implementation of this project would be less harmful for the environment (except CO2 emission to the atmosphere due to fuel burning by 500 icebreakers during 10 years) than other projects discussed earlier because ocean water would be freely circulating between the Arctic and North Atlantic. The navigation conditions along the Northern Sea Route would not be as favorable as it is currently. On the other hand, this could be regulated by periodical release of sea ice from the Arctic when needed. The most important problem is these icebreakers would not have the power to stop sea ice drift whose energy would be enormous (but could be estimated, of course).
Scenes from Around the Ship







Comments